
COVID misinformation being spread by numerous websites, analysis finds
Amid rising concerns over misinformation online - including surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic, especially vaccines - Americans are now a bit more open to the idea of the U.S. government taking steps to restrict false information online.And a majority of the public continues to favor technology companies taking such action, according to a new Pew Research Center survey.

Misinformation targeted by Stirling researcher About University of Stirling
Some people share misinformation accidentally, but others do so knowingly. To fully understand the spread of misinformation online, it is important to analyze those who purposely share it. Using a 2022 U.S. survey, we found that 14 percent of respondents reported knowingly sharing misinformation, and that these respondents were more likely to also report support

Reducing the Spread of Misinformation Online Markkula Center for Applied Ethics
Misinformation: Spreading false information (rumors, insults, and pranks). Disinformation: The creation and distribution of intentionally false information, usually for political ends (scams, hoaxes, forgeries). Infodemic: World Health Organization defines an infodemic as "an overabundance of information—some accurate and some not—that.

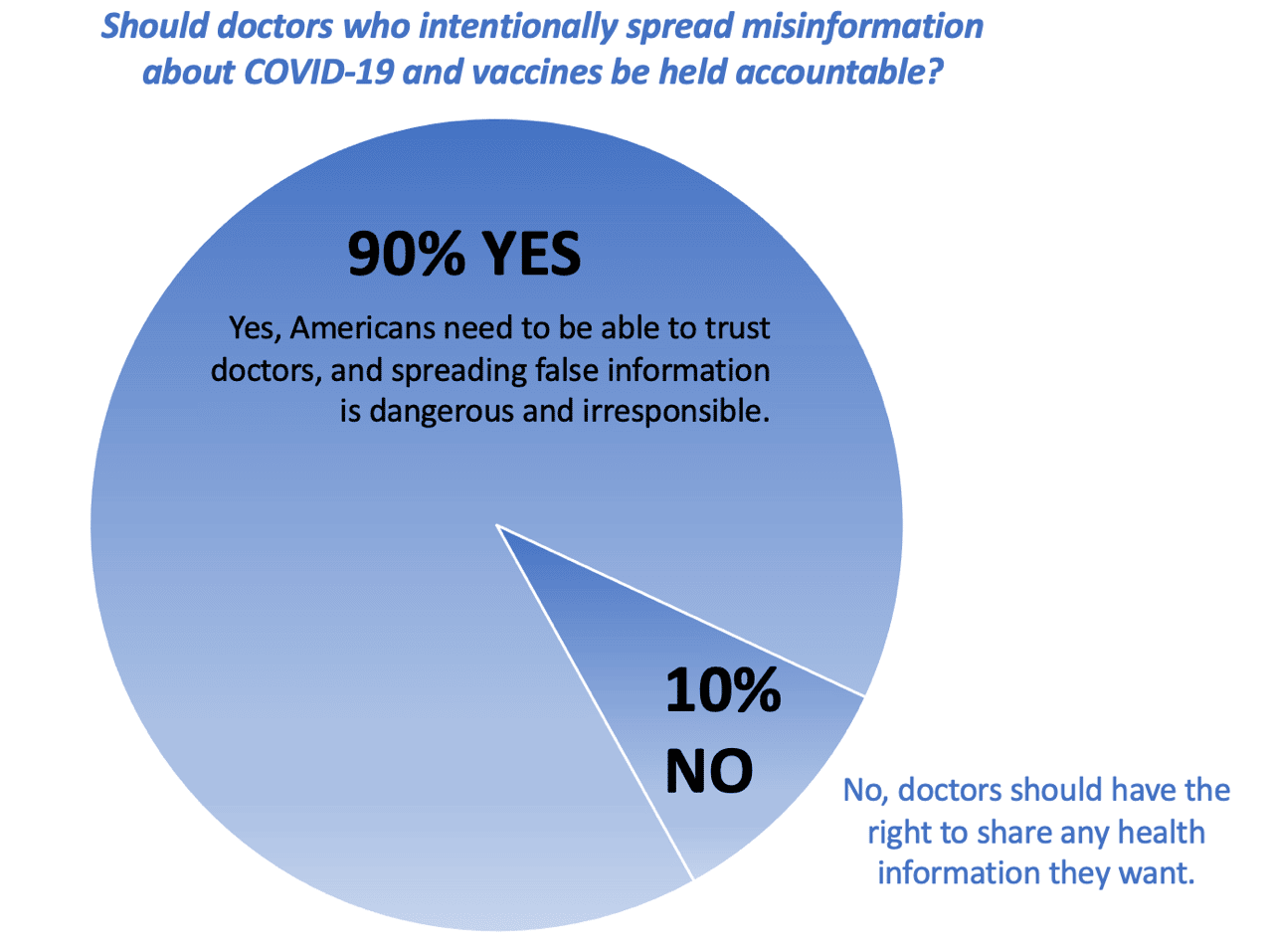
Is Spreading Medical Misinformation a Doctor’s Free Speech Right? The New York Times
The story had been pushed by aides and allies of then-President Donald J. Trump. By Ben Smith. Nov. 28, 2021. On Friday afternoons this fall, top American news executives have dialed into a series.

YouTube May Have Misinformation Blind Spots, Researchers Say The New York Times
Efforts to strategically spread false information online are dangerous and spreading fast. In 2018, a global inventory of social media manipulation found evidence of formally organized disinformation campaigns in forty-eight nations, up from twenty-one a year earlier. 1 While disinformation is not new, the ways in which it is now created and spread online, especially through social media.

Seven ways to protect yourself against misinformation Knowledge Enterprise
How to Deal With a Crisis of Misinformation. False news is on the rise. We can fight the spread with a simple exercise: Slow down and be skeptical. There's a disease that has been spreading for.

How to spot misinformation and stop its spread The Washington Post
As widespread as misinformation online is, opportunities to glimpse it in action are fairly rare. Yet shortly after the recent attack in Toronto, a journalist unwittingly carried out a kind of.
New Report Disinformation Doctors Licensed to Mislead de Beaumont Foundation
Misinformation shared on social media websites has fueled an epidemic of false belief, with widespread misconceptions concerning topics ranging from the COVID-19 pandemic to voter fraud, whether.

As Covid19 Continues to Spread, So Does Misinformation About It The New York Times
Misinformation has a growing impact on our lives and communities today, and could become a decisive issue in the 2024 presidential election.. pointing to the spread of misinformation currently occurring in the Middle East. Yamil Ricardo Velez, assistant professor of Political Science at Columbia, shared that while he acknowledged Schiffrin.

COVID19 misinformation How to spot it on your timeline
The mechanics of how misinformation and disinformation spread has long been an active area of research. According to the 'illusory truth effect', people perceive something to be true the more.

Recognize Misinformation on the The New York Times
The contemporary information landscape brings particular challenges: the internet and social media have enabled an exponential increase in misinformation spread and targeting to precise audiences.

haley⁷ on Twitter "me when I purposely spread misinformation on the / Twitter
Social media outperformed television as the major news source for young people of the UK and the USA. 10 Moreover, as it is easier to generate and disseminate news online than with traditional media or face to face, large volumes of fake news are produced online for many reasons (Shu et al. 2017).Furthermore, it has been reported in a previous study about the spread of online news on Twitter.
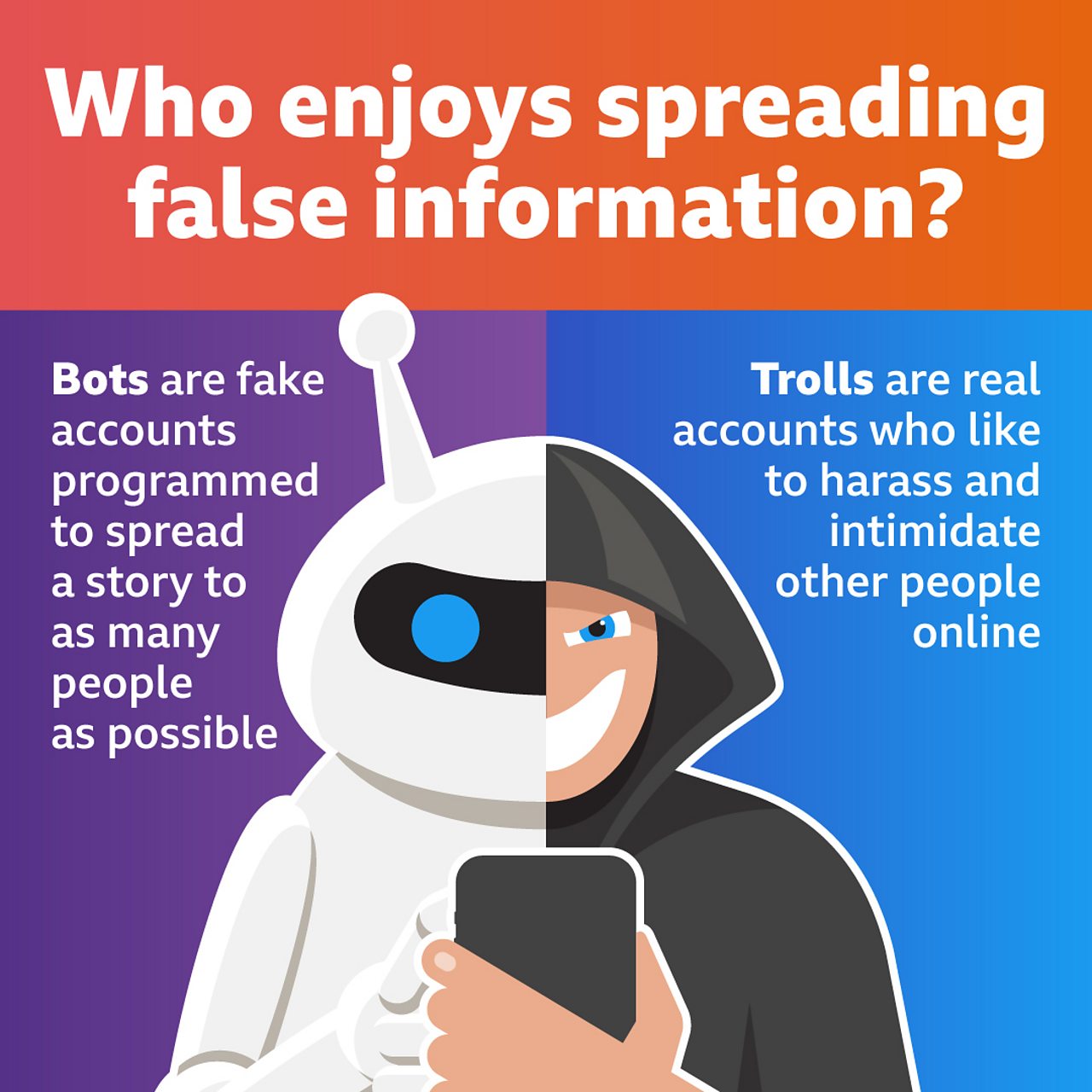
How false information spreads BBC Bitesize
Misinformation — false or inaccurate information of all kinds, from honest mistakes to conspiracy theories — and its more intentional subset, disinformation, are both thriving, fueled by a once-in-a-generation pandemic, extreme political polarization and a brave new world of social media. The psychology and politics of conspiracy theories

Dakota Johnson's joke about Armie Harmer gone wrong Entertainment News Gaga Daily
Starbird's group partnered with Stanford Internet Observatory on the Election Integrity Partnership ahead of the 2020 elections - a campaign during which a flood of misinformation swirled.

How to avoid disinformation and misinformation on Facebook and Twitter
PUBLISHED: 21 December 2021 LAST UPDATED: 26 January 2023 What is disinformation? Disinformation is false or misleading information, created to influence people. It can take many different forms and existed well before the internet.

Home Fake News Subject and Course Guides at University of Texas at Arlington
Published August 19, 2022 AARP/Getty Images In 1993, The New Yorker magazine published a cartoon with the caption, "On the Internet, nobody knows you're a dog." Almost 30 years later, that line might be rewritten: "On the internet, nobody knows who you are or that what you are saying is true."