
Free Duck Life Cycle and Anatomy Duck Book List Duck Unit Study Life cycles, Life cycles
Life Cycles Standards Life Science Plants and animals change as they grow and have different life cycles. Parents and their offspring have behaviors that help offspring survive. Key Words baby animals bills down duckling eggs fledglings hatch marsh migrate pond webbed feet Think Sheets Switch to Spanish
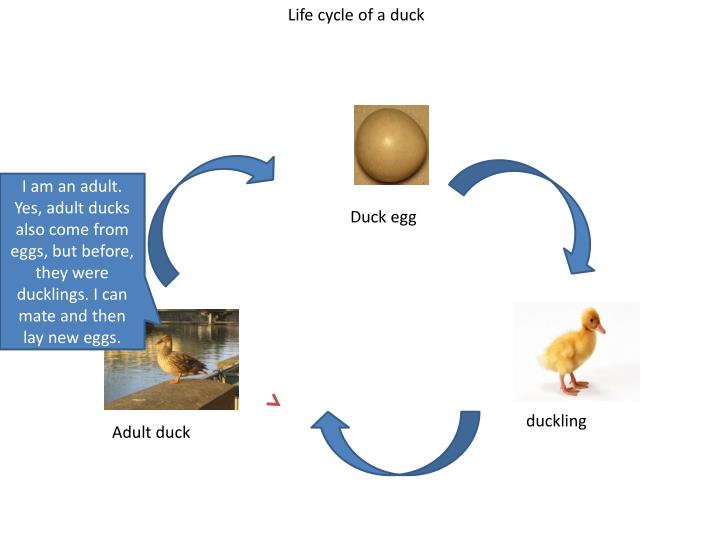
PPT Life cycle of a duck PowerPoint Presentation ID4915278
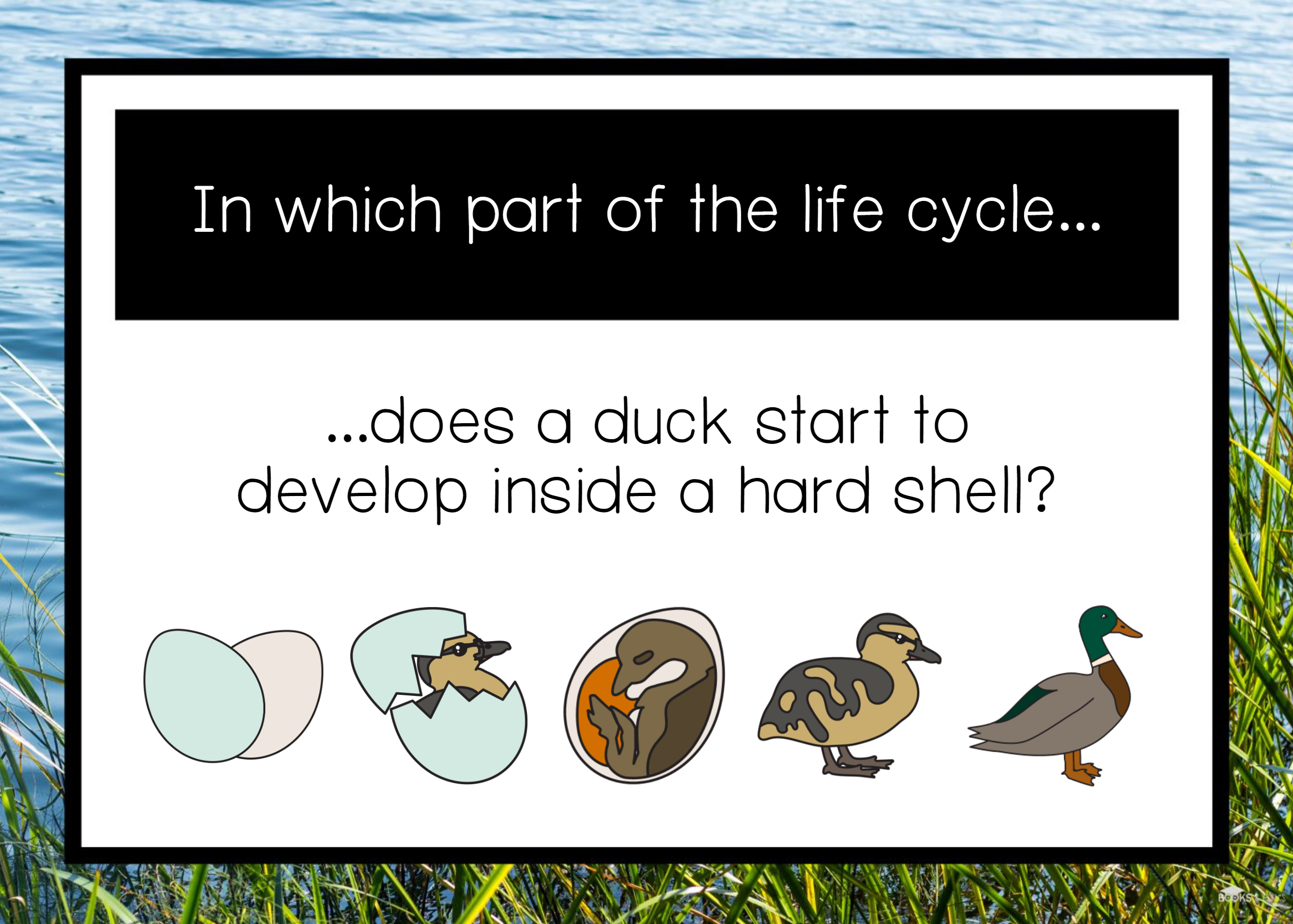
For waterfowl, the cycle of life begins anew each year with the eggs that are laid and carefully nurtured by nesting birds on their breeding grounds. An egg consists of three main parts: the yolk, albumen (egg white), and shell. Everything a duckling needs for its development is contained within these three components.
Life cycle of a duck Science ShowMe
February 21, 2022 by Holly Duffy Migratory waterfowl, like ducks, are considered to be among the most transient creatures in the natural world. But, while ducks are often on the move, the daily routine of a duck can be very predictable because it is usually based around two activities: eating and resting (what a life!).
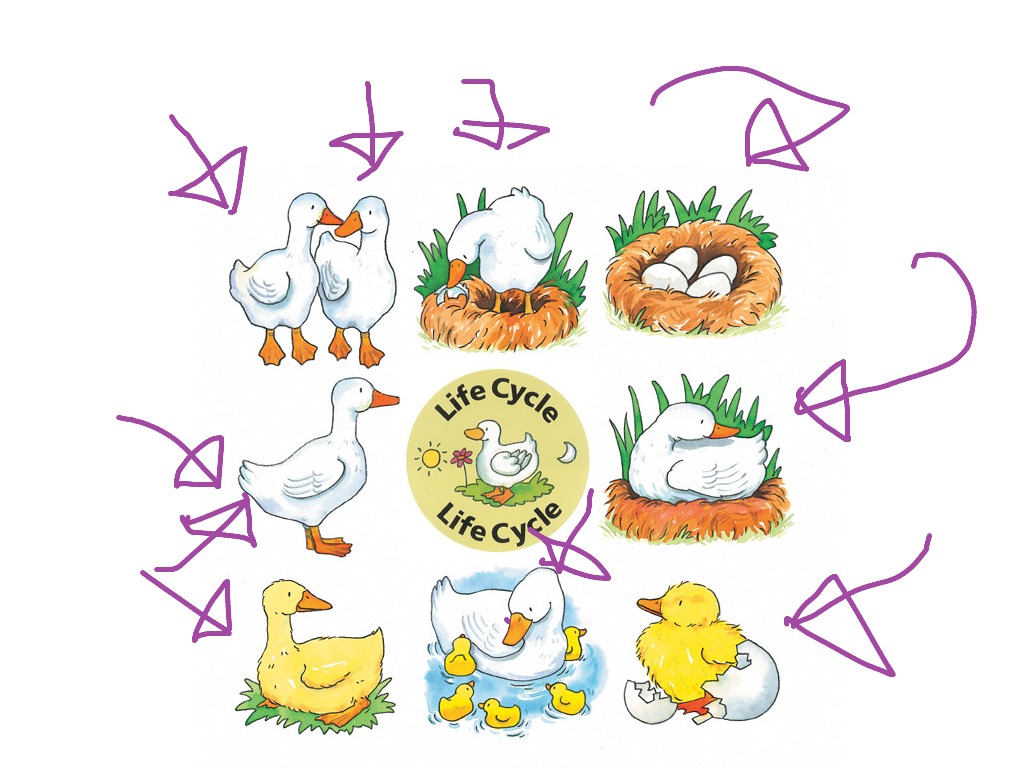
Duck life cycle book and lesson ideas. — Books & Bytes Canada
Perhaps the most familiar of all ducks, Mallards occur throughout North America and Eurasia in ponds and parks as well as wilder wetlands and estuaries. The male's gleaming green head, gray flanks, and black tail-curl arguably make it the most easily identified duck. Mallards have long been hunted for the table, and almost all domestic ducks.
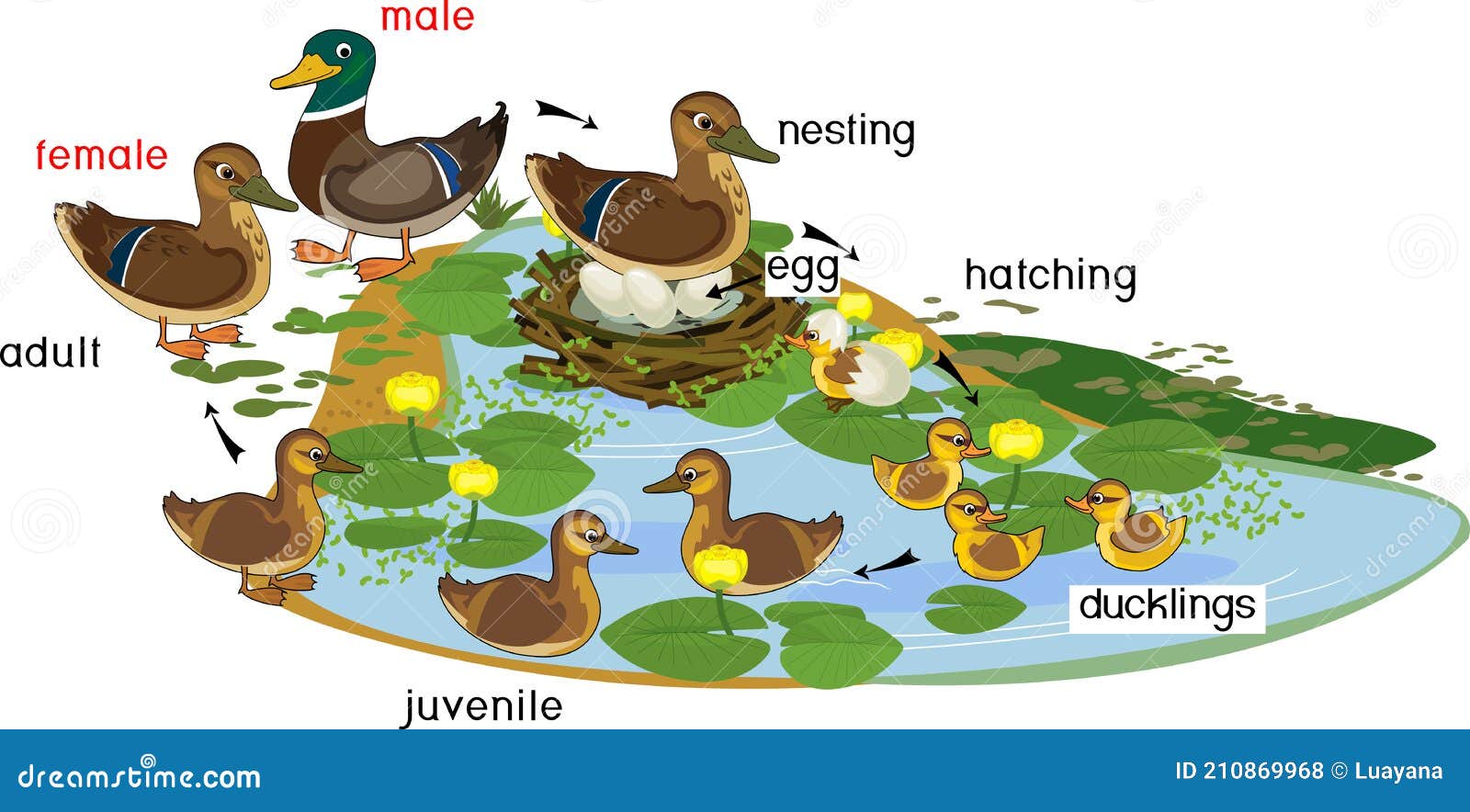
Pond with Life Cycle of Wild Ducks Mallard or Anas Platyrhynchos. Stock Vector Illustration of
Domestic ducks have a longer lifespan than their wild counterparts. The average lifespan of a domestic duck is between 8 to 10 years, but some breeds can live for up to 15 years. Bantam ducks have the longest life expectancy among all duck breeds, with some living up to 12 years.

PPT Life cycle of a duck PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4915278
The mallard is also the ancestor of the domestic duck which is a common poultry and ornamental bird all over the globe. Mallards have been recorded to live for nearly 30 years in the wild, although the average individual is not likely to reach the age of two. In captivity, mallards are likely to survive longer than wild birds if given good care.
Duck life cycle book and lesson ideas. — Books & Bytes Canada
The life cycle of a duck is a captivating journey that begins with the female duck laying her eggs in a concealed nest near water. The eggs then hatch, revealing adorable ducklings that quickly learn to swim and find food with their mother's guidance. As they mature, their downy feathers are replaced by the elegant plumage of adulthood.

How Things Grow The Life Cycle of a Duck (Paperback)
Updated Dec 1, 2021 Whether you brought home fertilized eggs or day-old ducklings, learning the duck development stages will help you better understand how to care for your new pets. From incubation to hatching and early life, baby duck breeds are living creatures whose specific needs must be met in order to thrive in a home environment.
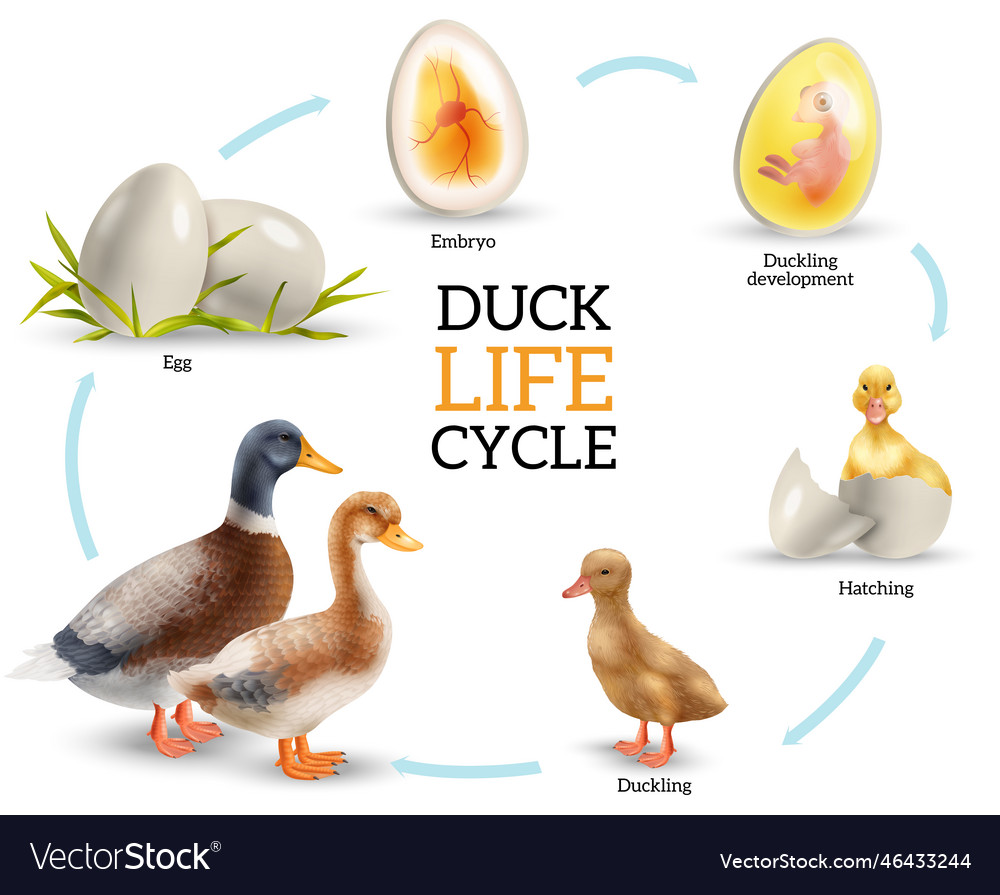
Duck life cycle infographics Royalty Free Vector Image
The Life Cycle of a Mallard Duck Mallard ducks are the most common species Of duck found in the United Kingdom. Let's take a 100k at the life cycle Of this amazing duck. Finding a Mate Mallard ducks 100k for a mate in late Winter. Male ducks are called drakes. They bob their heads up and down, fluff up their feathers and whistle to

Hand drawn duck life cycle Vector illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
Explore the complete life cycle of ducks, including nesting, migration, molting, and more. Gain insights into their breeding habits and wintering patterns. April 04, 2006 • 6 min read In the space of one year a duck experiences the full spectrum of seasonal changes that usher in opportunities and challenges.

Duck LifeCycle Custom Graphics Set!!! Birds Ducks for Preschool Pinterest
The life cycle of a duck includes nesting, brood rearing, post-breeding, molting, fall migration, winter migration, spring migration and pre-nesting. These cycles occur yearly until death, with most domestic ducks living no more than seven years. Ducks look for their mates in the fall and are usually part of an established pair by winter.

Life cycle of a duck Royalty Free Vector Image
Five Stages The Five Stages of Duck. What is the life cycle of a mallard duck? The adulthood age for mallards is fourteen months, and the average life expectancy is three years, but they can live to twenty. Several species of duck have brown-plumaged females that can be confused with the female mallard. Do ducks get pregnant?
The Life Cycle of a Duck Spring, duckling by robbyn Teaching Resources Tes
In the wild, the lifespan of ducks is typically between 5 and 10 years. In captivity, the outlook is more encouraging, with many domestically raised ducks living for up to 20 years or more. Wild ducks, and ducklings in particular, are relatively easy prey for many larger birds, and survival rates of new hatchlings can be as low as 10 percent.
Emma duck life cycle Science ShowMe
The life cycle of baby ducks includes growth, migration and parenting. Life cycle of ducks: eggs The mother of a duckling is a devoted parent. Once they have found the perfect spot for their nest, they settle for an extended period of nest-sitting, serving as the incubator for the baby ducklings growing inside the eggs.
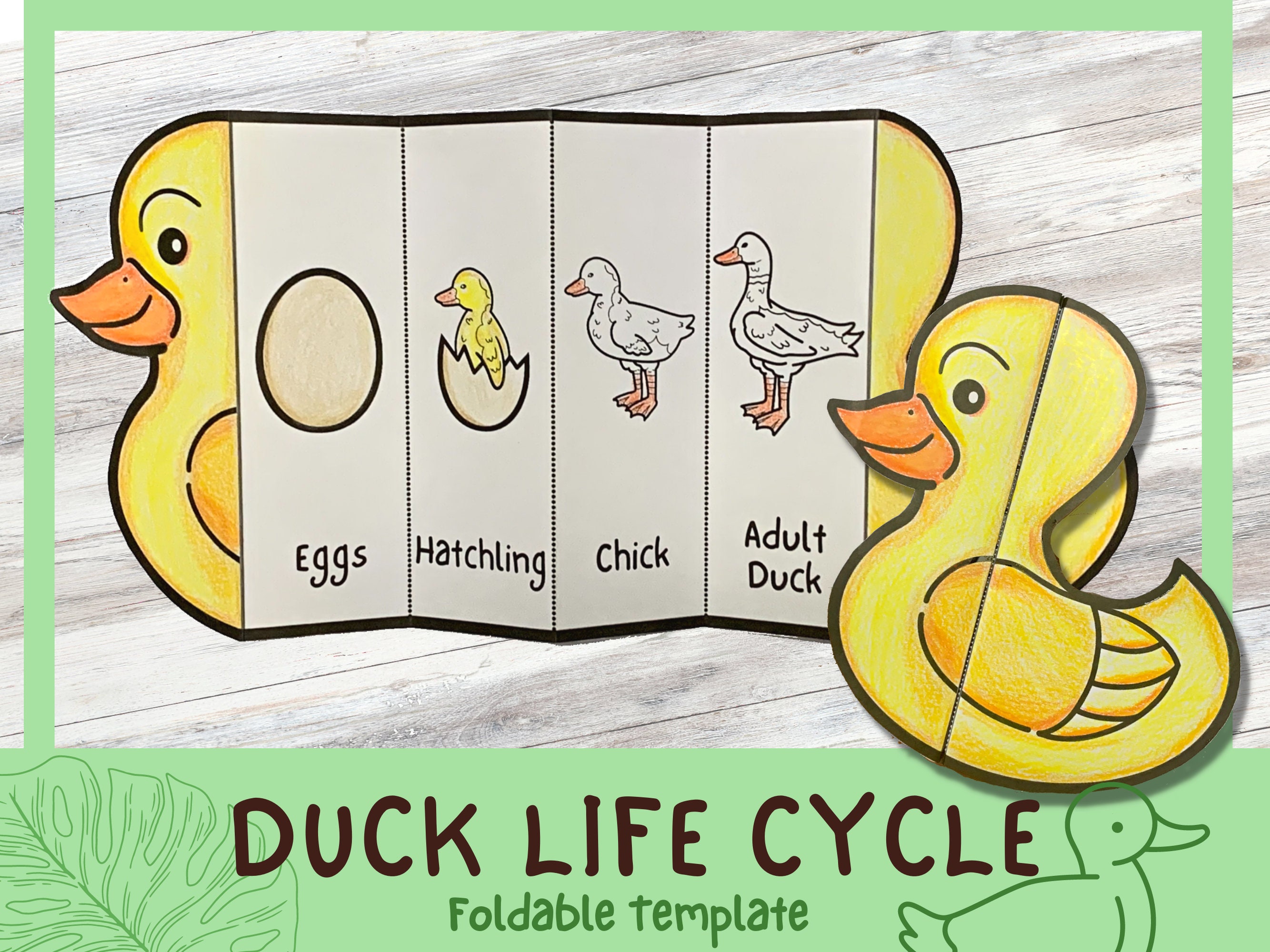
Foldable Duck Life Cycle Learning Activity for Kids A4 and Etsy UK
Duck Life Cycle: Incubation Period Most ducks create a nest out of vegetation. Mallards, for example, don't pluck or collect material and carry it to their nest but pull up all the vegetation that they can reach from the edge of the nest. Some ducks also pull the overhanging grasses and shrubbery over themselves to hide from predators.

Life cycle of a duck foldable sequencing activity Teaching Resources
Duck feathers have two basic adaptations. The first is an oily coating that prevents water from settling in duck feathers. Staying dry helps ducks stay warm and also decreases their body weight, which improves movement through the water and the air. Color is another common adaptation. The feathers of mallard ducks match the colors of the areas.